The third UK Shelter Forum PechaKucha, hosted by University College London, was held in London on the 12th March 2014. To apply for a place to present at the PechaKucha participants submitted posters. Using the PechaKucha format of 20 slides each shown for 20 seconds, ten speakers then presented their research into different aspects of shelter, settlements and disasters. Spot yourself in the photos here or watch the videos here.
Ana Gatóo, Cambridge University
Video I Email I Website I LinkedIn I Twitter
The Philippines Sheltering Response: three months after typhoon Haiyan
This presentation focuses on a fieldwork conducted on the Philippines in February 2014. During the fieldtrip, different actors involved in the humanitarian shelter response (government, NGOs and communities) were reached. The aim of those encounters was to find out the main issues that the organisations are facing and how ‘ReFocus’ (a group of researchers from the University of Cambridge) could assist them in their sheltering programme process. The findings that will be shown in this presentation are part of a longer report, which will be available here.
Elizabeth Wagemann, Cambridge University
Video I Email I Website I LinkedIn I Twitter
Implementing academic research: a pathway for impact
This talk focuses on the implementation of academic research relying on my research group’s experience. Academic research, driven by the generation of knowledge and innovative solutions, often do not share the aims and timelines of organisations involved in the reconstruction. Technical language does not harness the potential of research and outcomes stay in hands of specialists and libraries. Building on our report from the Phillipines after the Typhoon Haiyan, we draw examples of how to change the standard research model to enable a better flow of information and enhancement of the impact through partnerships with communities, governments and non-governmental organisations.
Catherine Crawford, UCL, and Alice Samson, Cambridge University
Video I Email I Website I LinkedIn I Twitter
Dialogue between archaeology and humanitarian shelter: resilience in pre-Columbian house-building and repair
This analysis of a “Caribbean architectural mode” – recurring house features, evidenced through excavations across the Caribbean (1400 BP- 450 BP) suggested that fundamental change in houses were less frequent but renewal and repair more frequent and more curious than humanitarian conceptions allow. Dialogue meant going beyond details of individual house objects – isolated (archaeologists) or designed/uniform (humanitarians) – to modes, shared across time, between people, constituting and catalysing wider change; and to house trajectories relating to processes and scales, eg regional environmental change, that are in train before and continue after “humanitarian history” begins at the moment of disaster.
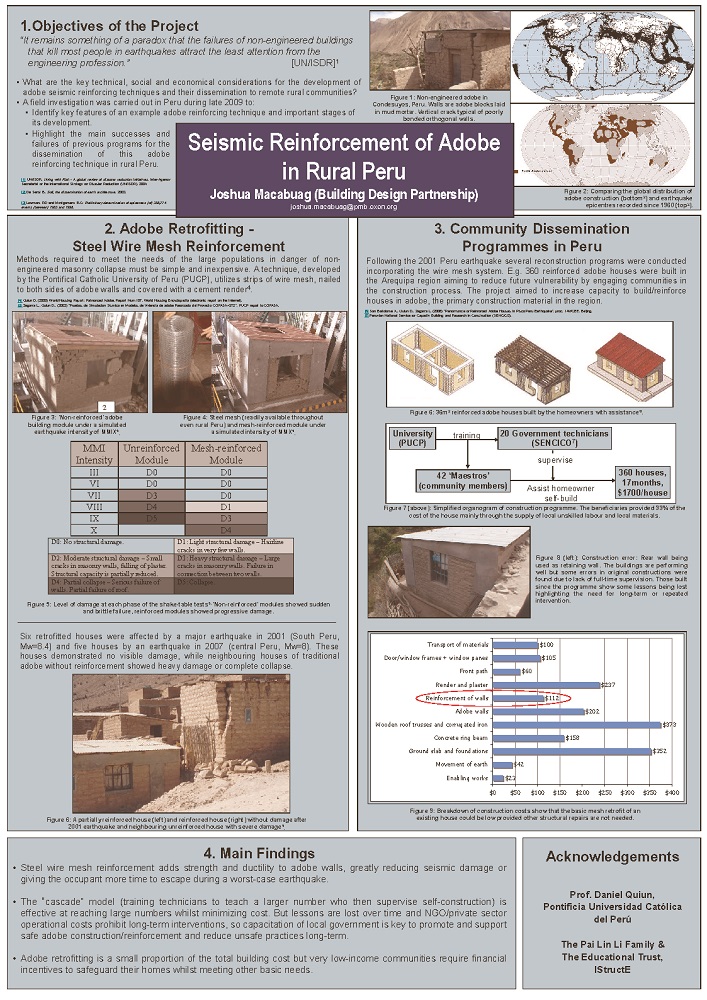
Josh Macabuag, UCL
Video I Email I Website I LinkedIn I Twitter
Seismic Retrofitting in Rural Communities
One of the greatest causes of casualties in major earthquakes around the world is the collapse of non-engineered masonry buildings (those built without engineering input). A barrier to realising research in this field is the significant social and economic challenge of implementation in low-income communities, where non-engineered housing is prevalent. The aim of this presentation is to give an overview of some of the technical, financial and social aspects of development and implementation of seismic retrofitting techniques in rural communities. The presentation describes: 1) The development (testing and analysis) of a particular seismic retrofitting technique 2) A pilot-project for implementation of that retrofitting technique in rural Nepal 3) A field investigation in rural Peru into the successes and failures of previous programmes for the dissemination of retrofitting techniques/skills to rural communities. Further details are available here and here.
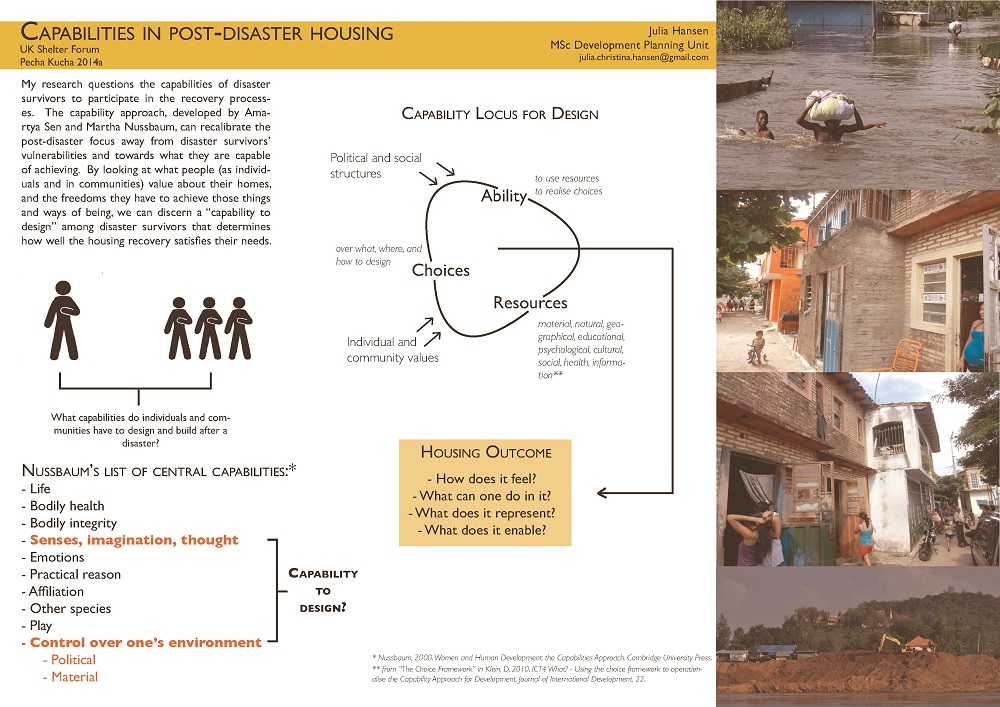
Julia Hansen, UCL
Video I Email I Website I LinkedIn I Twitter
Capabilities in post-disaster housing
My research questions the capabilities of disaster survivors to participate in the recovery processes. The capability approach, developed by Amartya Sen and Martha Nussbaum, can recalibrate the post-disaster focus away from disaster survivors’ vulnerabilities and towards what they are capable of achieving. By looking at what people (as individuals and in communities) value about their homes, and the freedoms they have to achieve those things and ways of being, we can discern a “design capability” among disaster survivors that determines how well the housing recovery satisfies their needs.
Ryan Sommerville, Westminster
Video I Email I Website I LinkedIn I Twitter
Preparing for post-disaster recovery: Open Data, Community and Built Environment Professionals
This presentation is a brief summary of current work by the Humanitarian OpenStreetMap Team, The World Bank, UN-HABITAT and others. It highlights the use of OpenStreetMap as an open source, crowd sourced platform to geo-reference data; at tool for participatory mapping. The presentation then suggests that there is a role for Built Environment Professionals to use (or assist in the use of) this methodology for participatory mapping of critical infrastructure. The data gathered will then inform emergency response following a disaster. This presentation also suggests there is potential to expand this methodology for use in early recovery. It is noted that further research is necessary to determine the current level of use (particularly by UN-HABITAT) and specifically identify areas of involvement for Built Environment Professionals to assist in pre- and post-disaster decision-making.
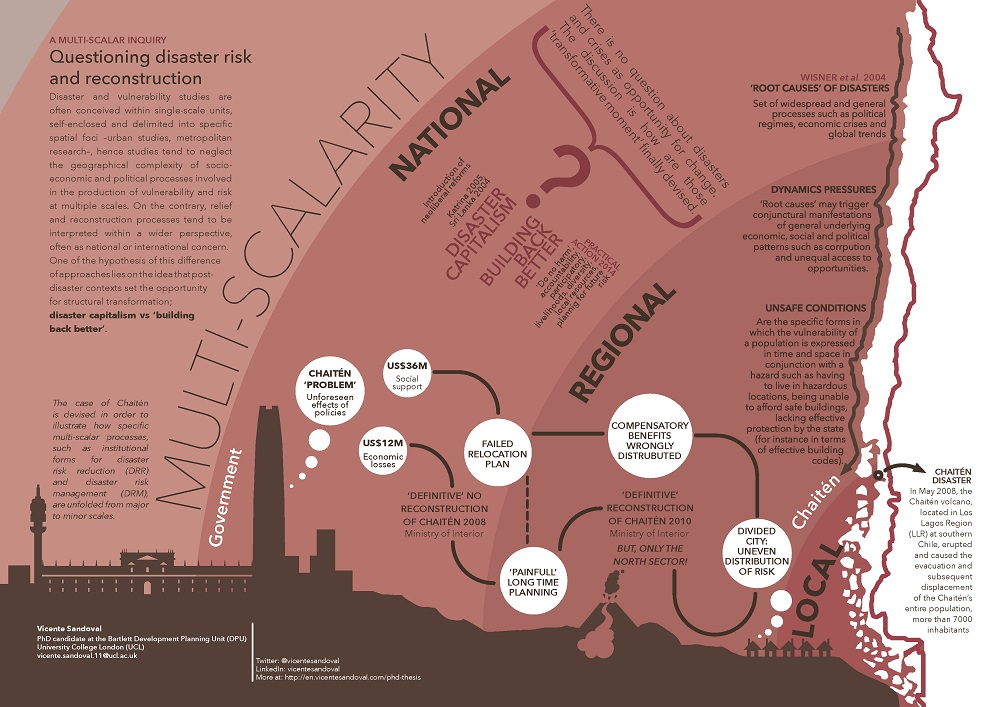
Vicente Sandoval, UCL
Video I Email I Website I LinkedIn I Twitter
Questioning disaster risk and reconstruction: A multi-scalar inquiry
Disaster and vulnerability studies are often conceived within single-scale units, self-enclosed and delimited into specific spatial foci –urban studies, metropolitan research–, hence studies tend to neglect the geographical complexity of socio-economic and political processes involved in the production of vulnerability and risk at multiple scales. On the contrary, relief and reconstruction processes tend to be interpreted within a wider perspective, often as national or international concern. One of the hypotheses of this difference of approaches lies on the idea that post-disaster contexts set the opportunity for structural transformation; ‘disaster capitalism’ versus ‘building back better’.
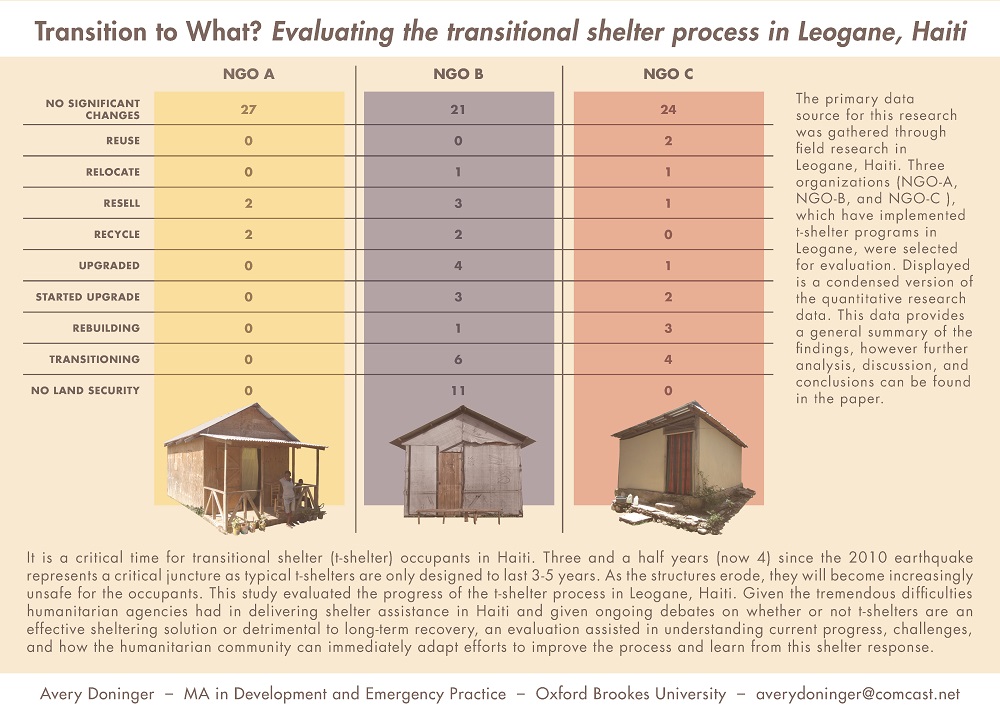
Avery Doninger, Oxford Brookes University
Video I Email I Website I LinkedIn I Twitter
‘Transition to What?’Evaluating the transitional shelterprocess in Leogane, Haiti
It is a critical time for transitional shelter (t-shelter) occupants in Haiti. Three and a half years (now 4) since the 2010 earthquake represents a critical juncture as typical t-shelters are only designed to last 3-5 years. As the structures erode, they will become increasingly unsafe for the occupants. This study evaluated the progress of the t-shelter process in Leogane, Haiti. Given the tremendous difficulties humanitarian agencies had in delivering shelter assistance in Haiti and given ongoing debates on whether or not t-shelters are an effective sheltering solution or detrimental to long-term recovery, an evaluation assisted in understanding current progress, challenges, and how the humanitarian community can immediately adapt efforts to improve the process and learn from this shelter response.
Martin Dolan, Oxford Brookes University
Video I Email I Website I LinkedIn I Twitter
How was the ‘social urbanism’ of Medellin made possible?
The social urbanism of Medellin is being hailed as a miracle of urban design and slum upgrade. The city which was infamous as the most violent city in the world until the dramatic change of the last ten years under the progressive mayor Sergio Fajardo. Crime rates are no only 10% of what they used to be and the quality of life has risen dramatically. This presentation examines the physical, political and economic ways this was made possible, not all of them very conventional or ethical.
Pedro Clarke, Oxford Brookes University
Video I Email I Website I LinkedIn I Twitter
Learning from Disasters: Lisbon 1755
How the 1755 triple earthquake, tsunami and fire devastated Lisbon and how the city (slowly) but surely reinvented itself.
Aditya Aachi, Architectural Association
Video I Email I Website I LinkedIn I Twitter
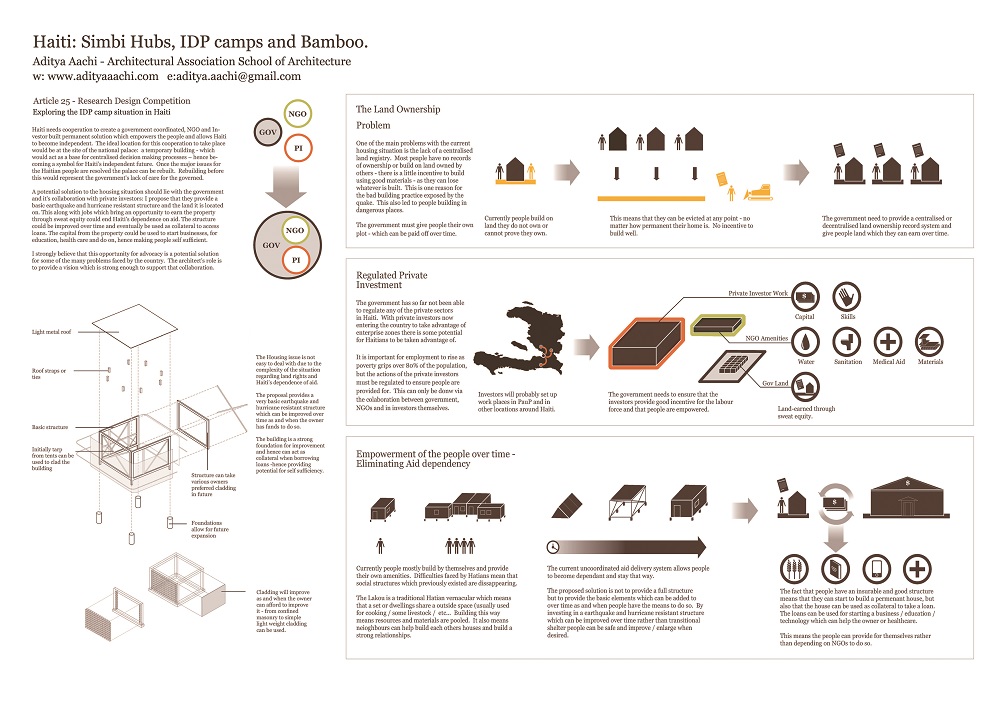
Haiti: Simbi Hubs, IDP camps and Bamboo
Theoretical proposal for water and sanitation infrastructure in post earthquake Port-au-Prince. Exploration of the IDP camp situation. Architectural bamboo workshop in Port-au-Prince which took place in January 2014.
This event was organised by Victoria Maynard, Bernadette Devilat and Chris Sinclair with funding from the Public Engagement Unit at University College London.